Change Linux File Permissions With chmod
Linux is a multi user OS which means that it supports multiple users at a time. As many people can access the system simultaneously and some resources are shared, Linux controls access through ownership and permissions.
Linux file ownership
In Linux, there are three types of owners: user, group, and others .
Linux User
A user is the default owner and creator of the file. So this user is called owner as well.
Linux Group
A user-group is a collection of users. Users that belonging to a group will have the same Linux group permissions to access a file/ folder. You can use groups to assign permissions in a bulk instead of assigning them individually. A user can belong to more than one group as well.
Other
Any users that are not part of the user or group classes belong to this class.
Linux File Permissions
File permissions fall in three categories: read, write, and execute.
Read permission
For regular files, read permissions allow users to open and read the file only. Users can't modify the file.
Similarly for directories, read permissions allow the listing of directory content without any modification in the directory.
Write permission
When files have write permissions, the user can modify (edit, delete) the file and save it.
For folders, write permissions enable a user to modify its contents (create, delete, and rename the files inside it), and modify the contents of files that the user has write permissions to.
Execute permission
For files, execute permissions allows the user to run an executable script. For directories, the user can access them, and access details about files in the directory.
How do I change directory permissions in Linux?
To change directory permissions in Linux, use the following:- chmod +rwx filename to add permissions
- chmod -rwx directoryname to remove permissions.
- chmod +x filename to allow executable permissions.
- chmod -wx filename to take out write and executable permissions.
How to Change Directory Permissions in Linux for the Group Owners and Others
The command for changing directory permissions for group owners is similar, but add a “g” for group or “o” for users:- chmod g+w filename
- chmod g-wx filename
- chmod o+w filename
- chmod o-rwx foldername
- chmod ugo+rwx foldername to give read, write, and execute to everyone.
- chmod a=r foldername to give only read permission for everyone.
-
To change directory permissions for everyone, use “u” for users, “g” for group, “o” for others, and “ugo” or “a” (for all).
How to Change Groups of Files and Directories in Linux
By issuing these commands, you can change groups of files and directories in Linux.- chgrp groupname filename
- chgrp groupname foldername
How to change ownership in Linux
Another helpful command is changing ownerships of files and directories in Linux:- chown name filename
- chown name foldername These commands will give ownership to someone, but all sub files and directories still belong to the original owner. You can also combine the group and ownership command by using:
- chown -R name:filename /home/name/directoryname
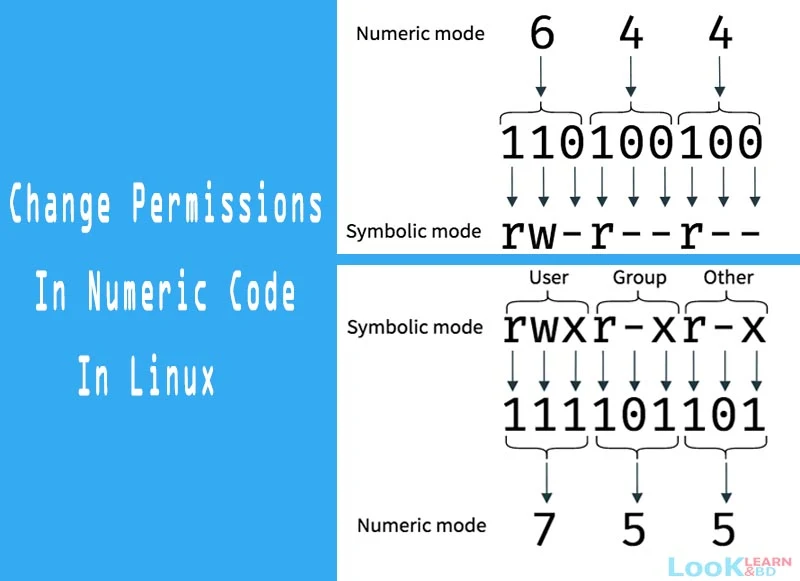
How to change permissions in numeric code in Linux
You may need to know how to change permissions in numeric code in Linux, so to do this you use numbers instead of “r”, “w”, or “x”.- 0 = No Permission
- 1 = Execute
- 2 = Write
- 4 = Read
Permission numbers are:
- 0 = ---
- 1 = --x
- 2 = -w-
- 3 = -wx
- 4 = r-
- 5 = r-x
- 6 = rw-
- 7 = rwx
For example:
- chmod 777 foldername will give read, write, and execute permissions for everyone.
- chmod 700 foldername will give read, write, and execute permissions for the user only.
- chmod 327 foldername will give write and execute (3) permission for the user, w (2) for the group, and read, write, and execute for the users.